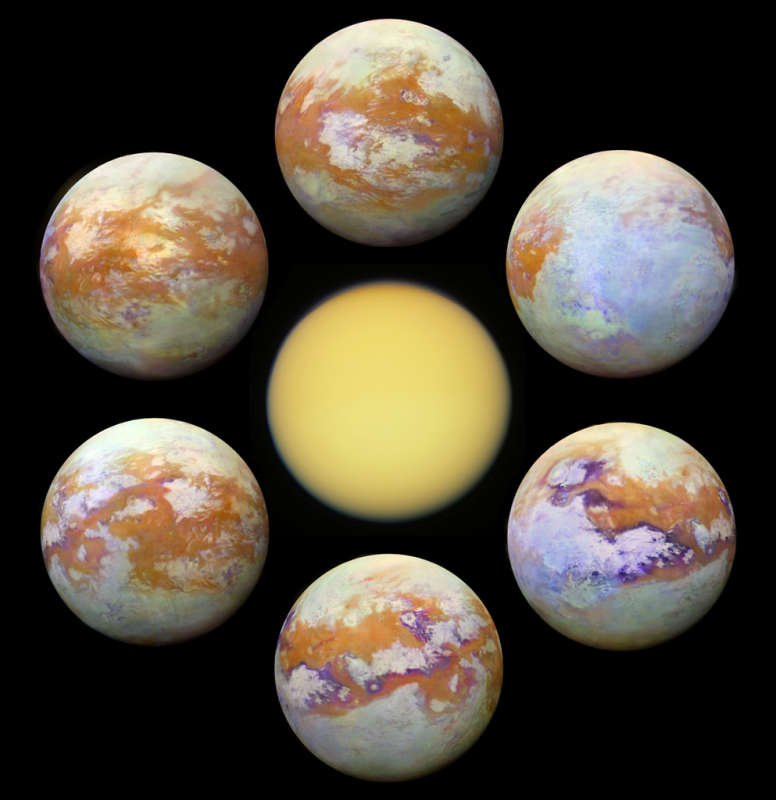
Explanation: Shrouded in a thick atmosphere, Saturn's largest moon Titan really is hard to see. Small particles suspended in the upper atmosphere cause an almost impenetrable haze, strongly scattering light at visible wavelengths and hiding Titan's surface features from prying eyes. But Titan's surface is better imaged at infrared wavelengths where scattering is weaker and atmospheric absorption is reduced. Arrayed around this visible light image (center) of Titan are some of the clearest global infrared views of the tantalizing moon so far. In false color, the six panels present a consistent processing of 13 years of infrared image data from the Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) on board the Cassini spacecraft orbiting Saturn from 2004 to 2017. They offer a stunning comparison with Cassini's visible light view. NASA's revolutionary rotorcraft mission to Titan is due to launch in 2027.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
Titan - Титан
Публикации со словами: Titan - Титан | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |