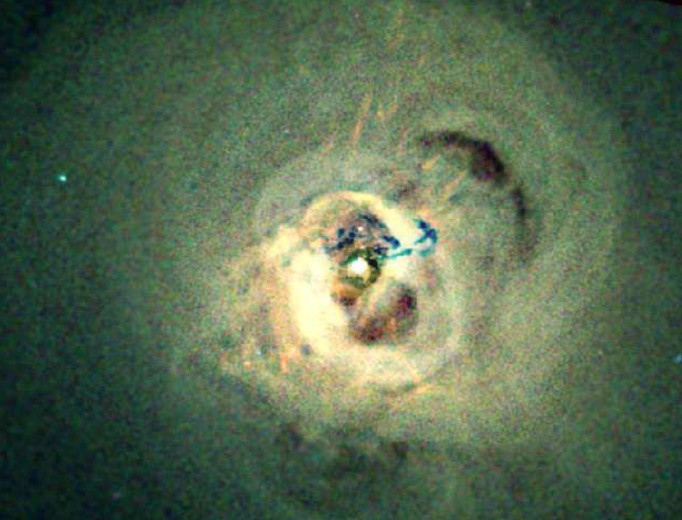
Explanation: The Perseus Cluster of thousands of galaxies, 250 million light-years distant, is one of the most massive objects in the Universe and the brightest galaxy cluster in the x-ray sky. At its core lies the giant cannibal galaxy Perseus A (NGC 1275), accreting matter as gas and galaxies fall into it. This deep Chandra Observatory x-ray image spans about 300,000 light-years across the galaxy cluster core. It shows remarkable details of x-ray emission from the monster galaxy and surrounding hot (30-70 million degrees C) cluster gas. The bright central source is the supermassive black hole at the core of Perseus A itself. Low density regions are seen as dark bubbles or voids, believed to be generated by cyclic outbursts of activity from the central black hole. The activity creates pressure waves - sound waves on a cosmic scale- that ripple through the x-ray hot gas. Dramatically, the blue-green wisps just above centre in the false-color view are likely x-ray shadows of the remains of a small galaxy falling into the burgeoning Perseus A.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
Perseus A - NGC 1275 - galaxy cluster - Perseus cluster - Скопление галактик - скопление персея - active galaxy - Персей А - рентгеновское излучение - активная галактика
Публикации со словами: Perseus A - NGC 1275 - galaxy cluster - Perseus cluster - Скопление галактик - скопление персея - active galaxy - Персей А - рентгеновское излучение - активная галактика | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |