Credit & Copyright: Optical: R.P.van der Marel & J.Gerssen
(STScI),
NASA;
X-ray: S.Komossa & G.Hasinger (MPE) et al., CXC, NASA
Explanation:
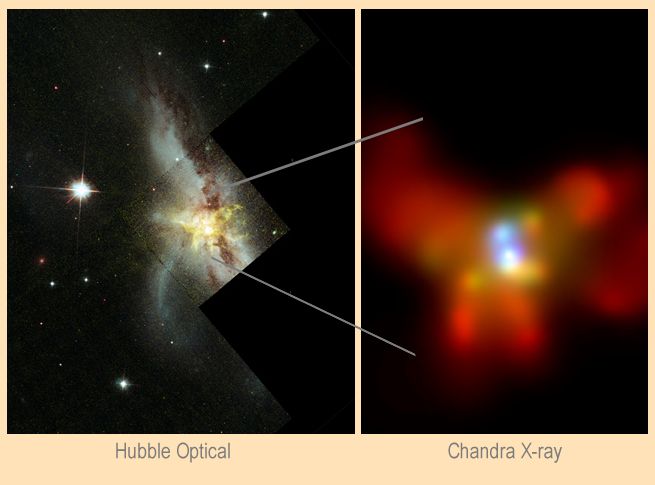
The
Hubble optical image on the left shows
NGC 6240 in
the throes of a
titanic galaxy - galaxy collision 400 million light-years away.
As the cosmic catastrophe plays out, the merging galaxies spew forth
distorted tidal tails
of stars, gas, and dust and undergo
frantic bursts of star formation.
Using the orbiting
Chandra
Observatory's x-ray vision to peer within
the bright central regions of NGC 6242 astronomers
believe they have uncovered,
for
the first time, not one but
two enormous orbiting black holes, by
detecting the characteristic x-ray radiation from the interstellar debris
swirling toward them.
In the false-color close-up view at right,
the x-ray data clearly show
the black hole sources (shaded blue) separated by about 3,000 light-years.
Einstein's theory of gravity predicts that such a pair of black holes
must spiral closer together, and
ultimately coalesce into a single,
even more massive black hole
after
several hundred million
years.
In the final moments the merging supermassive black holes will
produce an extremely powerful burst of
gravitational radiation.
X-ray: S.Komossa & G.Hasinger (MPE) et al., CXC, NASA
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
NGC 6240 - black hole - черные дыры - рентгеновское излучение
Публикации со словами: NGC 6240 - black hole - черные дыры - рентгеновское излучение | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |