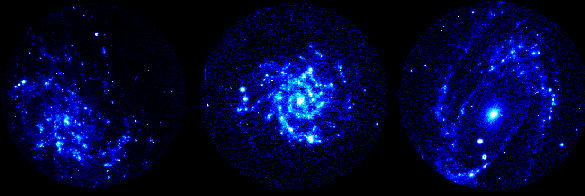
Explanation: A progression of beautiful spiral galaxies is illustrated above with three photographs from NASA's Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT). Flying above the Earth's obscuring layer of atmosphere on the Space Shuttle Columbia during the Astro-1 mission in 1990, UIT's cameras were able to image these distant spirals in the ultraviolet light produced by hot, young stars. These bright stars, newly condensed from gas and dust clouds, give away the location of the spiral arms they are born in. Because they are massive (many times the mass of the Sun), they are shortlived. Dying and fading before they move too far from their birth place they make excellent tracers of spiral structure. From left to right the galaxies are known as M33, M74, and M81 and have progressively more tightly wound spiral arms. Astronomers would classify these as Scd, Sc, and Sb type spirals using a galaxy classification scheme first worked out by Edwin Hubble.
Information:
The
Scale of the Universe Debate in April 1996
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
spiral galaxy - спиральная галактика - Спиральные ветви галактик - Ультрафиолетовое излучение - молодые звезды
Публикации со словами: spiral galaxy - спиральная галактика - Спиральные ветви галактик - Ультрафиолетовое излучение - молодые звезды | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |