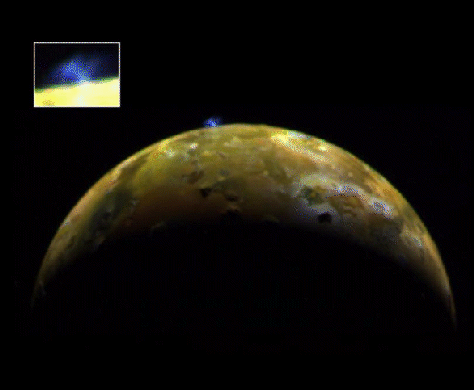
Explanation: Io's surface is active. Geyser-like eruptions from volcanoes on this Jovian moon were seen by both Voyager spacecraft in 1979 and were also spotted this year in late June by Galileo's camera from a distance of about 600,000 miles. The blue plume seen at the moon's edge (magnified in the inset) arises from Ra Patera, a large shield volcano, and extends about 60 miles above the surface. The blue color is attributed to condensing and freezing sulfur dioxide gas. Galileo images have also revealed that the plume glows in the dark - perhaps due to fluorescence of excited sulfur and oxygen ions. Io's surface is cold, its temperature averages about -230 degrees Fahrenheit, so why is it so active? The most likely cause is the gravitational tug of war over Io between Jupiter and the other Galilean moons which perturbs Io's orbit. The orbital changes would result in tidal force variations heating Io's interior and and generating the sulfurous volcanic activity.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
галилеевы спутники - вулкан - извержение - КА Вояджер - КА Галилео
Публикации со словами: галилеевы спутники - вулкан - извержение - КА Вояджер - КА Галилео | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |